Led display work under high temperature conditions for a long time will cause the lamp beads to decay and reduce the lifespan. At the same time, the probability of failure rate of electronic devices will increase rapidly. As a result, the display reliability is reduced. So solving the problem of LED display heat dissipation is a very important part of the LED display production. So what kind of design can reduce costs and increase efficiency?
A, thermal design knowledge
Two basic laws of heat transfer: Heat flows from the high temperature zone to the low temperature zone; heat emitted from the high temperature zone equals the heat absorbed in the low temperature zone.
There are three basic ways of transferring heat: heat conduction, convection, and radiation.
Thermal Conductivity: Gas heat conduction is the result of collisions between gas molecules as they move irregularly. Thermal conduction in metallic conductors is mainly accomplished by the movement of free electrons. The heat conduction in a non-conductive solid is achieved by the vibration of the lattice structure. The heat conduction mechanism in the liquid mainly depends on the action of the elastic wave.
Convection: Refers to the process of heat transfer caused by the relative displacement between various parts of the fluid. Convection occurs only in fluids and must be accompanied by heat conduction. The heat exchange process that occurs when a fluid flows over the surface of an object is called convection heat transfer. The convection caused by the different densities of the hot and cold parts of the fluid is called natural convection. If fluid motion is caused by external forces (fans, etc.), it is called forced convection.
Radiation: The process of an object's ability to transmit in the form of electromagnetic waves is called thermal radiation. Radiant energy transfers energy in a vacuum, and there is a conversion in the form of energy, that is, heat energy is converted into radiation energy and radiation energy is converted into heat energy.
When selecting the heat dissipation mode, the following factors should be considered: heat flux density, volume power density, total power consumption, surface area, volume, working environment conditions (temperature, humidity, air pressure, dust, etc.) of the led display.
According to the heat transfer mechanism, there are natural cooling, forced air cooling, direct liquid cooling, evaporative cooling, thermoelectric cooling, and heat pipe heat transfer.
Common heat dissipation methods are compared as follows:
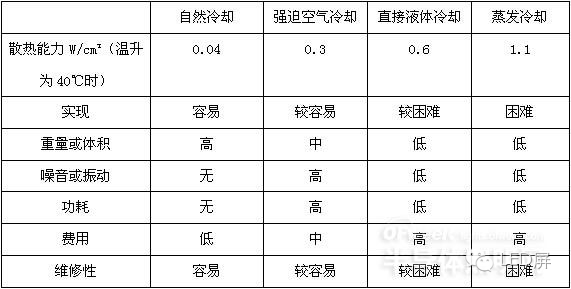
Natural Cooling Forced Air Cooling Direct Liquid Cooling Evaporative Cooling
Heat dissipation capacity W/cm? (When the temperature rises to 40°C) 0.040.30.61.1
It is easier and more difficult to achieve
Low or high weight or volume
No noise or vibration
Low power consumption
Low cost, high price
Maintenance is easier and more difficult than difficult
From the above table, it can be seen that natural cooling has a relatively small heat dissipation effect, and evaporative cooling has a relatively large heat dissipation effect. The human body sweats and cools, using the cooling method of evaporative cooling.
Second, led display thermal design methods
It can be known from practical applications that the current internal heat of the LED display is relatively high, and the electronic components with more heat are: LEDs, driver ICs, and switching power supplies. Therefore, it is necessary to design the heat dissipation of the led display screen to provide a low thermal resistance path between the heat source and the external environment so as to ensure smooth heat transfer.
When the object temperature is lower than 1800°C, the meaningful wavelength of heat radiation is between 0.38 and 100 μm, and most of the energy is in the infrared range of 0.76-20 μm. In the visible light range, the proportion of thermal radiation energy is not large. Therefore, the LED display can be coated with various colors. Direct sunlight outside the led display needs to be painted in light colors to avoid visible light absorption.
Considering the use of led display screens, leased screens and indoor fixed mounting screens are mostly cooled by natural cooling. Outdoor fixed mounting screens are often forced air cooling.
Outdoor fixed installation led display, in the entire screen installation, we must consider the thermal design. Due to the restriction of the installation site, as the power consumption of led display screens decreases, more and more customers will install LED display screens outdoors without any other auxiliary cooling measures. For the large screen led display, only natural cooling cooling, cooling capacity is relatively poor. Therefore, the thermal design of the LED display cabinet is particularly important. From the angle of reliability, maintenance cost and other aspects of the LED display cabinet, forced convection cooling with a fan is a good way to dissipate heat.
The heat exchange area between the heat-generating electronic components and the cool air, and the temperature difference between the heat-generating electronic components and the cool air directly affect the heat dissipation effect. This involves the design of the air volume entering the led display cabinet and the design of the air duct. When designing ventilation ducts, direct ducts should be used to transport air, avoiding sharp turning and curved ducts. Ventilation ducts should avoid sudden expansion or sudden contraction. Do not exceed 20 degrees of expansion angle? Do not shrink the taper angle greater than 60? . Ventilation ducts should be sealed as far as possible and all laps should follow the flow direction.
When designing a led display cabinet, there are a few points to note: The air inlet should be set on the underside of the cabinet, but not too low to prevent dirt and water from entering the cabinet installed on the floor. Vents should be located near the top of the box. The air should be circulated from below the tank and a dedicated inlet or exhaust hole should be used. Cooling air should be allowed to flow through the heat-generating electronic components while preventing a short circuit in the airflow. Air inlets and outlets must be provided with a filter to prevent debris from entering the cabinet. Natural convection should be designed to help force convection. The design must ensure that the air inlet and exhaust port are far away. Avoid using reusing cooling air. Taking into account the air volume expansion of the factors, the outlet area should be 1.5 times -2 times the area of ​​the inlet. Larger electronic components such as switching power supplies should be located as close to the air inlet as possible. To ensure that the radiator slot direction is parallel to the wind direction, the radiator slots cannot block the air path.
The fan is installed in the system. Due to the structural limitations, the air inlet and the air outlet are often subjected to various barriers, and their performance curves may change. According to practical experience, the inlet and outlet of the fan is preferably at a distance of 40 mm from the barrier, and if there is a space limitation, it should be at least 20 mm.
Choosing a fan is generally limited by the fan inlet and outlet air temperature. In the case of ventilation, because the fan draws hot air, the life of the fan will have a serious impact. For fan manufacturers, 60°C is generally used as the condition for calibrating fan life. If the ambient temperature of the fan is higher than 60°C, the fan life will be reduced by half every 5°C.
When considering the use of ventilation or air blowing, you can refer to the following table for comparison of air blowing and ventilation.
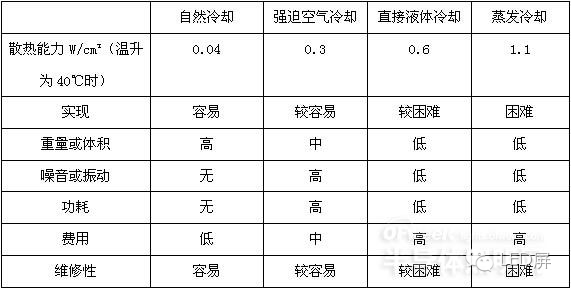
1 uneven air supply, hair has a certain degree of directionality, local heat transfer is strong, suitable for a more concentrated heating device. The air is evenly distributed, which is suitable for the more even distribution of heating devices and the complicated air duct.
2 The airflow near the fan outlet is mainly turbulent. The flow entering the fan is mainly laminar.
3 The fan operates at a lower air temperature and the fan has a longer life. Fans work at high temperatures at the air outlet, and their life will be affected.
4 When the air blows, a positive pressure is formed in the box to prevent the dust in the gap from entering the box. Negative pressure is formed in the cabinet, and dust in the gap enters the cabinet.
The thermal design of the module inside the box is also a consideration. Poor thermal design can result in poor display and smearing. When placing the heat-generating components on the PCB, consider the uniform distribution of heat as much as possible, and do not concentrate the components with a lot of heat on one part of the PCB.
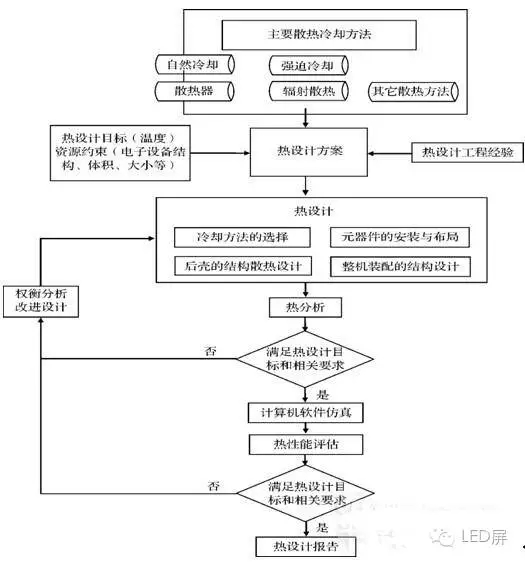
The following figure shows the cooling design flow chart
Third, led display thermal design example
In the following, the actual installed outdoor fixed-mounted LED display is taken as an example to discuss the heat dissipation design.
The above picture is the actual installation of Honghua Optoelectronics in Guangdong installed outdoor led display, model P10 outdoor surface mount full color, brightness of 5500cd, maximum power of 923W. Led display screen cooling method for natural cooling. Comprehensive heat dissipation cost and quality considerations, the cooling mode of the led display cabinet is fan air forced cooling.
First calculate the air to flow rate, the formula is L = Wr / (CÏ (tn-tl))
L: Air to flow, m3/s; Wr: Air forced cooling to dissipate heat; C: Specific heat of air, kJ/(kg°C); Ï: Density of air, kg/m3;tn: Inside temperature of cabinet, °C; Tl: cool air temperature input by the cooling system, °C
According to the above formula, we can know that if you want to ensure that the air temperature inside the led display box does not exceed tn °C, the cooling system needs to input cold air into the air volume Wr ​​/ (CÏ (tn-tl)) m3 / s.
Assume that the heat dissipation capacity of the LED display panel is W, taking into account that natural cooling, radiation, and heat dissipation play a very small role in the entire heat dissipation process of the cabinet. We will consider W as the forced air cooling and heat dissipation. Accurately calculating the internal heat output of the led display is not easy to implement in engineering, usually using the estimation method. It is known from experience that when the still white screen is played with the maximum brightness, the A1688 heating power is about 300 W, that is, Wr = 0.3 KW. Under normal circumstances, led display, LED light source heat accounted for about 45% of the entire screen heat, the driver part of the heat accounted for about 50% of the entire screen, the controller and cable, etc. accounted for about 5% of the entire screen heat.
The specific heat capacity of air and the density of air are related to the temperature, humidity and pressure of air. Check the local historical climate data, taking into account the most unfavorable climatic conditions, determine C=0.7kJ/(kg°C) and Ï=0.7kg/m3.
The internal temperature tn of the box refers to the maximum air temperature inside the box, usually in the upper part of the box. Check the specifications of electronic components such as switching power supplies and driver ICs and determine that tn is 60°C.
According to the local climatic data and installation characteristics, it is determined that the cooling air input temperature of the cooling system tl is 40°C.
L=0.3/(0.7*0.7*(60-40))=0.031m3/s
Then calculate the fan opening area and fan selection.
Depending on the location of the installation site, heat dissipation via fan blowing is used.
Select the company's common fan, air volume is 50CFM, converted to 0.023m3/s. Therefore, use two fans to blow air.
The design behind the box is shown in the figure above.
After the design is completed, actual test verification is required. Test results are shown in the table below.
Experimental temperature recording table (unit °C, experimental conditions: 40 °C high temperature room, brightness 12000nit, all white static screen)
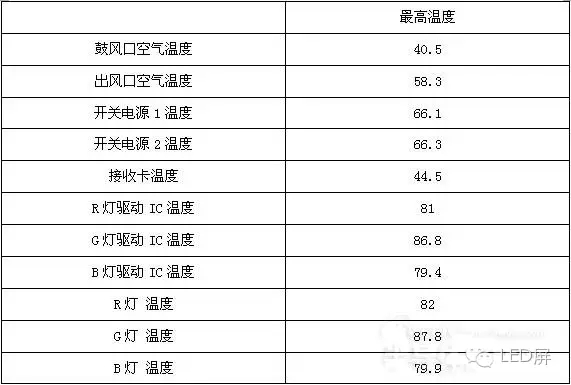
Highest temperature
Air outlet air temperature 40.5
Outlet air temperature 58.3
Switching power supply 1 temperature 66.1
Switching power supply 2 temperature 66.3
Receiving card temperature 44.5
R lamp driver IC temperature 81
G lamp driver IC temperature 86.8
B lamp driver IC temperature 79.4
R lamp temperature 82
G lamp temperature 87.8
B lamp temperature 79.9
Through a good heat dissipation design, this led display installed in foreign countries has been operating stably and working normally for several years.
Fourth, the conclusion
Fourth, the conclusion
The high temperature has a greater impact on the reliability of the led display and requires thermal design. Outdoor fixed installation led display, starting from the heat dissipation design of the large screen, and then the heat dissipation design of the box, the thermal design of the module. Thermal design, you need to do the program first, calculate the no problem and then do prototype test verification. Test and verify the problem-free led display will not appear in the actual work of high temperature problems.
A gear or cogwheel is a rotating machine part having cut teeth, or cogs, which mesh with another toothed part to transmit torque. Geared devices can change the speed, torque, and direction of a power source. Gears almost always produce a change in torque, creating a mechanical advantage, through their gear ratio, and thus may be considered a simple machine. Terex Gear including Terex Pto Driven Gear;Terex Planetary Gear;Terex Sun Gear etc.
Terex Gear
Terex Gear,Terex Planetary Gear,Terex Sun Gear,Terex Pto Driven Gear
Chengdu Svoda Machinery Equipment Co.,Ltd , https://www.svdequip.com
